Introduction:
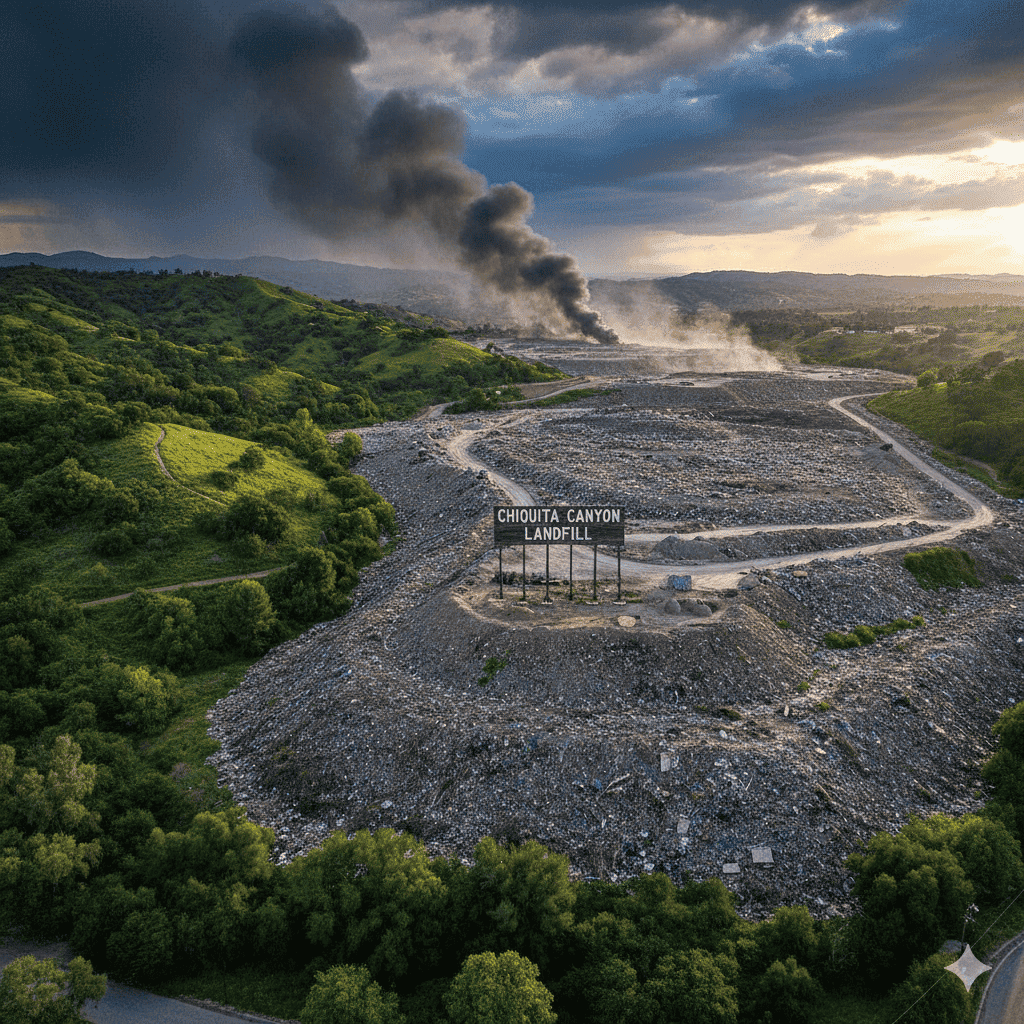
As the global population continues to expand, waste generation has reached record levels. Traditional landfills – once seen as simple dumping grounds – are now at the center of environmental, climate and public health concerns. In this new landscape of waste management, innovation is not a luxury; This is a necessity. One facility in the spotlight is the Chiquita Canyon Landfill in Castaic, California. The site has been scrutinized due to operational and environmental challenges, but it also has the untapped potential to become a leader in green landfill innovation.
The shift from old-fashioned landfill to sustainable waste management requires better technology, stronger enforcement of environmental standards and meaningful engagement with nearby communities. So, can the Chiquita Canyon Landfill be transformed from a problematic site into a beacon of clean, circular waste solutions? Let’s take a deeper look at the future of this feature.
A closer look: history and present status of Chiquita canyon
The Chiquita Canyon Landfill covers more than 600 acres and has been accepting municipal solid waste for over 50 years. For decades, it served as an important destination for Los Angeles County—an area where millions of residents generate enormous amounts of waste every day.
Although it has played an important role in urban waste management, landfills have also faced difficulties. One of the most worrying events was an increase in underground heat-related reaction known as a subsurface elevated temperature (SET) phenomenon, which produced intense odors, raised health concerns in nearby communities and required the intervention of regulators.
In addition, thousands of odor complaints have been lodged in surrounding communities in recent years – increasing public pressure on the landfill. The operator eventually stopped accepting new waste from January 1, 2025, and moved the facility into a shutdown and monitoring phase.
While this closure ends traditional waste operations, it also opens up a unique opportunity: the transition from landfill to innovation, environmental remediation and the foundation for a clean future.
What does green landfill innovation mean?
If the Chiquita Canyon Landfill is to be a leader, it must adopt technologies and strategies that significantly reduce environmental impact while providing new benefits. Green landfill innovations include:
1. Waste-to-energy technologies
Landfills produce methane – a powerful greenhouse gas. Capturing landfill gas and converting it into usable energy allows the site to:
• Reduce emissions
• Produce renewable energy
• Create income streams
This is a big step towards transforming landfills from pollutants into productive energy hubs.
2. Leachate control and groundwater conservation
Modern lining systems, drainage controls and treatment facilities are necessary to prevent pollution from liquids formed by the breakdown of waste.
3. Air quality and odor control system
Advanced monitoring, improved gas extraction and barrier technologies reduce off-site odors and ensure clean ambient air.
4. Promote a circular waste economy
A circular waste economy focuses on keeping materials in use for a longer period of time. This means less dumping and more:
• Recycling
• Treatment of organic waste (e.g. composting)
• Content recovery
This approach redefines landfills as waste diversion centers, not waste burial grounds.
5. Changes after closing
After uncovering and stabilization, landfill land can be reused:
• Solar energy farm
• Public green space
• Research and technology demonstration site
This transforms previous environmental impact into long-term societal value.
Current sustainability moves at Chiquita Canyon
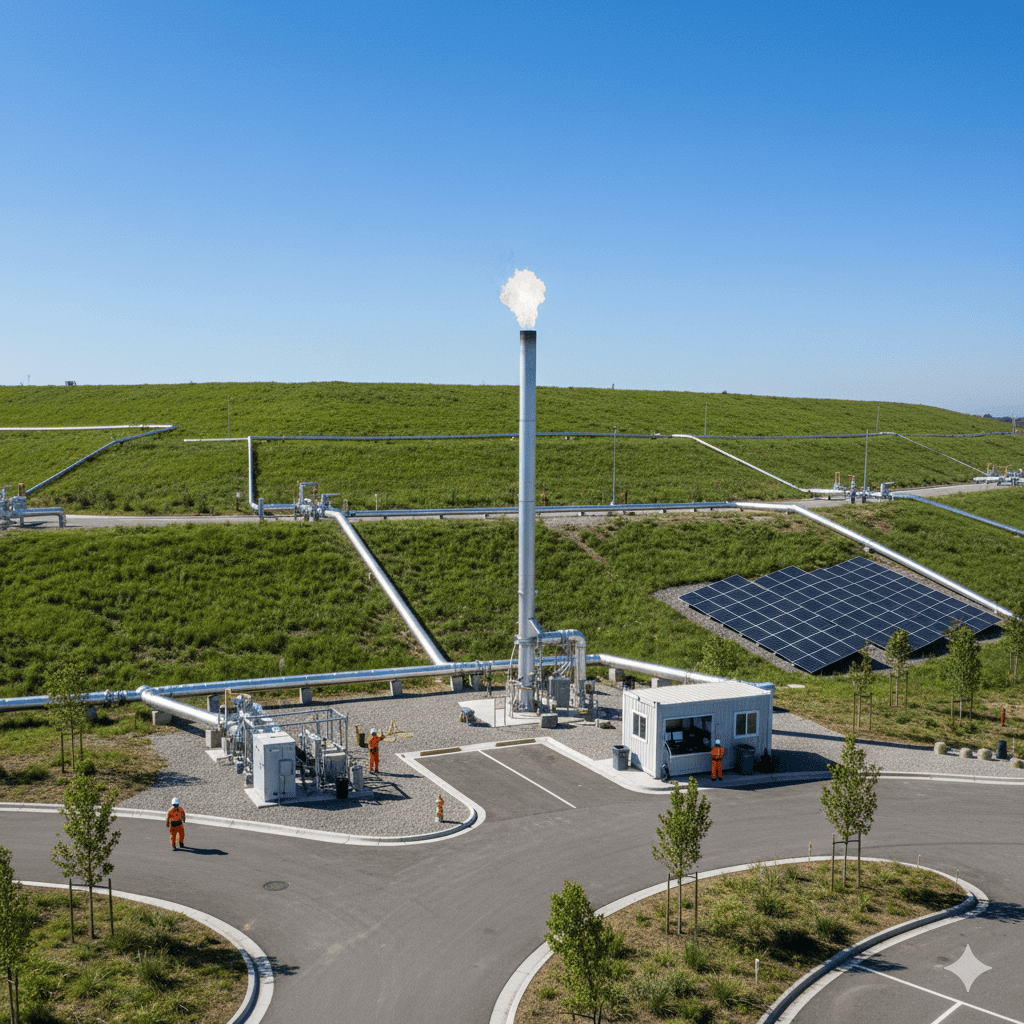

The landfill’s transition away from disposal suggests a new operational focus: environmental management and remediation. Several steps already show improvement:
1. Expanding cover system with high performance
2. Advanced monitoring of gas, odor and chemical production
3. Increased transparency in environmental reporting
4. Plan to terminate long-term engineering plans
5. Cooperate with regulators to control SET incidents
These are important foundations – but real leadership in innovation will require broader and bolder strategies.
Remaining barriers to progress
Despite the prospects, success is not guaranteed. Chiquita Canyon Landfill Still Struggling:
1. Community trust issues – Residents remain frustrated by odors and health issues
2. Regulatory challenges – Several breaches of environmental compliance must be resolved
3. Technical difficulties – the phenomenon of underground heating continues to require major interventions
4. Concerns about funding – transition to green innovation models requires significant
investment
A strong recovery and future leadership requires continuous improvements in transparency, accountability and environmental controls.
Opportunities for a greener future
With proper planning and commitment, the Chiquita Canyon Landfill has the potential to become a model for the future of the waste industry. Here’s how to do it:
1. Expansion of waste to energy technologies
Methane-to-power systems can allow landfills to produce clean energy for the local grid – turning old buried waste into a new source of electricity.
2. Create clean-energy land reuse
A closed landfill cap can support:
• Solar panel area
• Wind energy technology
• Infrastructure for battery storage
This positions the site as a climate-positive energy element.
3. Becoming a hub for the circular waste economy
Even without accepting new waste, the site can support regional recycling and processing of biodegradable materials – reducing future reliance on landfills across California.
4. Using smart monitoring technology
AI-based systems and real-time sensors can provide quick answers to:
• Temperature increases
• Increase in emissions
• Gas leak
This creates a safer environment and reduces long-term risks.
Prioritizing community health

Strong environmental justice programs can include:
• Improved odor suppression
• Research on health effects
• Projects that benefit the local community
This ensures that local communities become partners in landfill operations – not victims.
Climate financing and carbon credit opportunities
By capturing greenhouse gases and producing renewable energy, the landfill can earn carbon credits and sustainability funds.
Will Chiquita Canyon landfill lead the way?
The future direction of the site depends on three key commitments:
• Environmental excellence
• Completely solve emissions issues and the ongoing challenge of subsurface Enhanced Temperature (SET)
• Result: Restored public trust + long-term compliance with regulations
Financial investment
• Funding the development of modern waste-to-energy and recycling innovations
• Result: Local economic growth through new resource value
• Community partnership
• Transparent communication and active participation of surrounding communities
• Result: Decrease in public influence and shared decision-making
Potential transformation of Chiquita Canyon Landfill
If these obligations are met, the landfill can be transformed into the leading sustainability model of the future:
• From a simple landfill → a renewable energy generator
• From an environmental point of view → an environmental solution
• From the source of community conflict → a symbol of cooperation
Conclusion:
The landfill in Chiquita Canyon is at a critical juncture. Its history of operational problems and societal tensions cannot be ignored. But with bold infrastructure upgrades, green technologies and a strong emphasis on environmental justice, the landfill could become a powerful example of modern waste management development.
The future of waste is not only about where the waste goes –
• It’s about capturing energy
• Protect the planet
• Supports a sustainable circular economy
• And respect the communities that live nearby
If the approach is pursued aggressively and responsibly, Chiquita Canyon could become a global benchmark for green innovation in waste management – proving that even the most controversial landfills can be transformed into climate-positive assets for society.